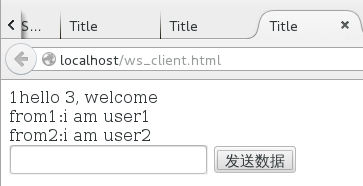
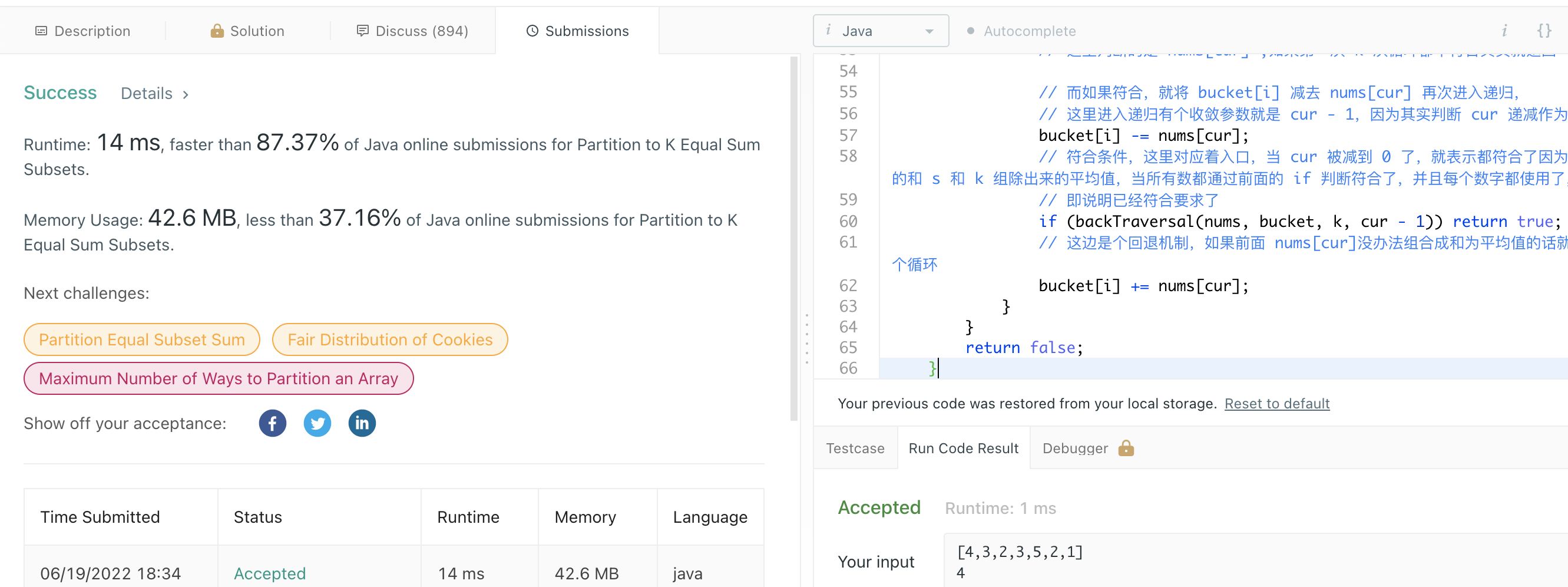
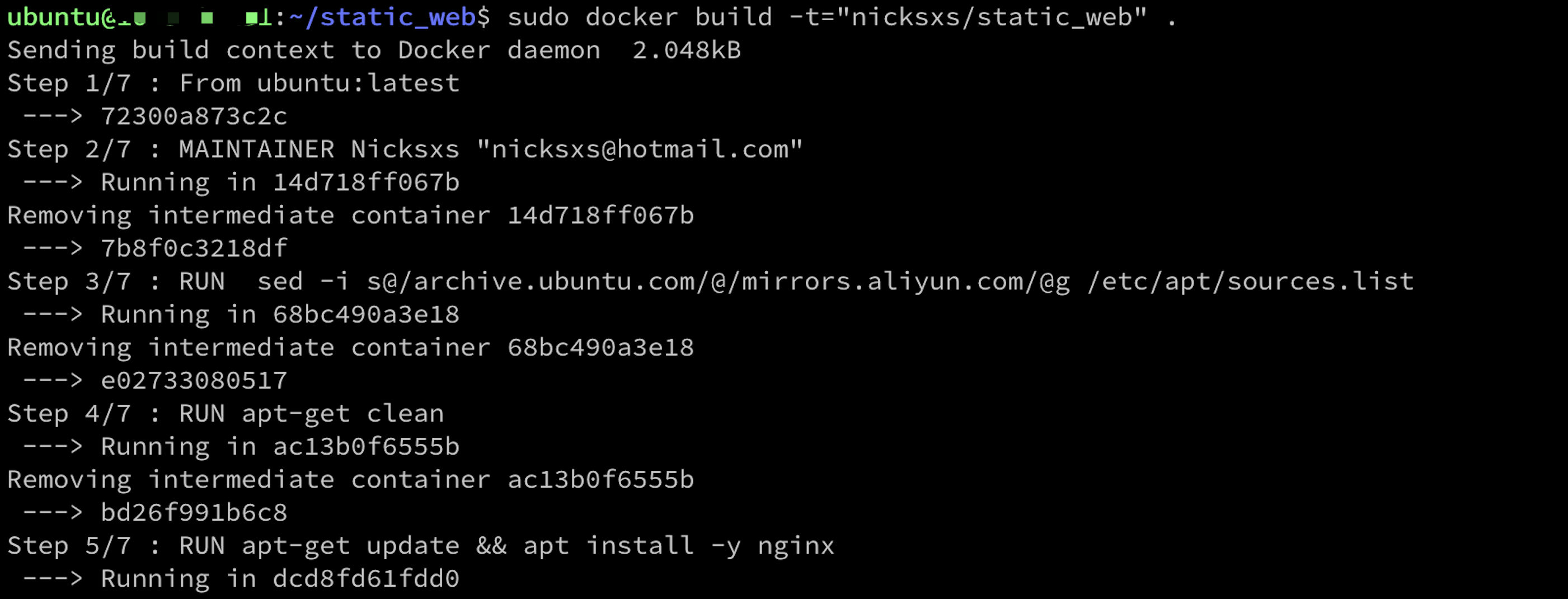
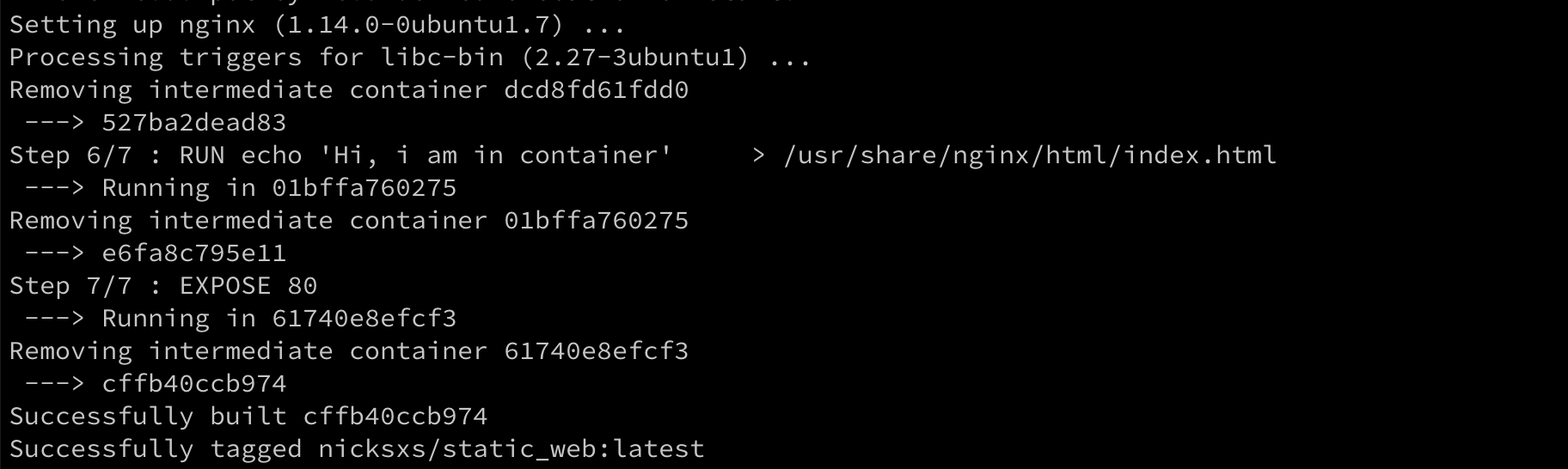
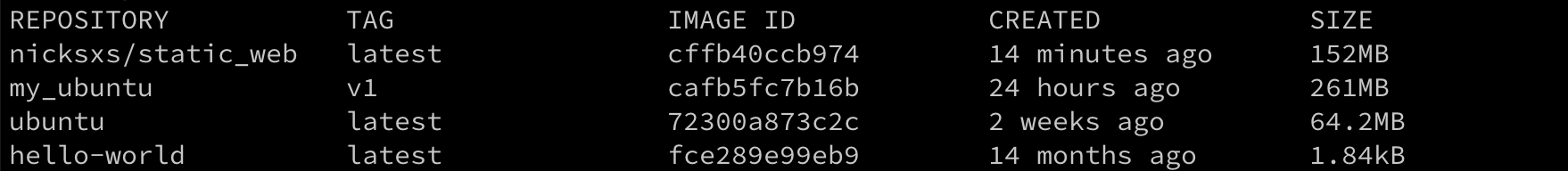
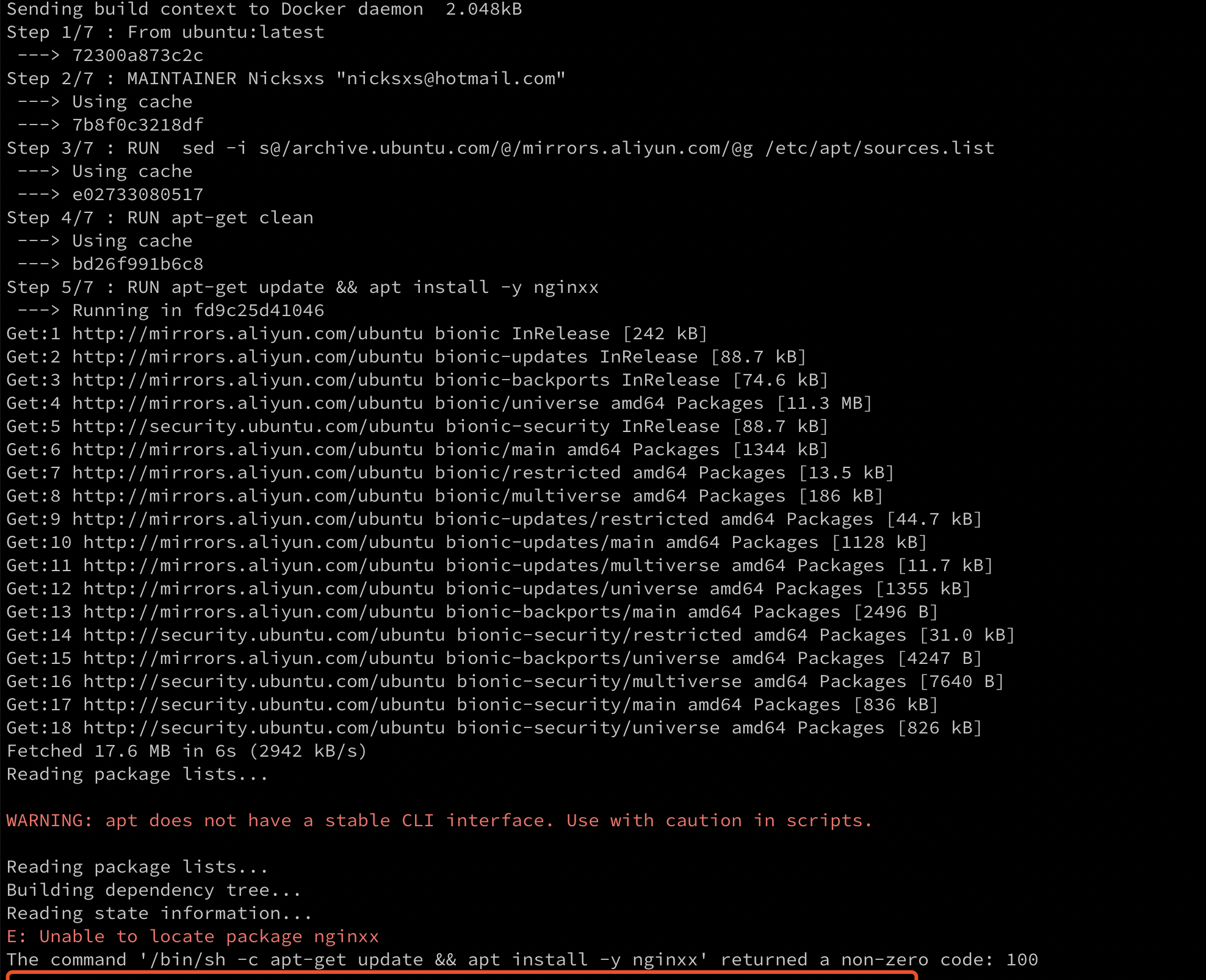
首先看下官方的小 demo
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, MQClientException {
/*
* Instantiate with specified consumer group name.
* 首先是new 一个对象出来,然后指定 Consumer 的 Group
* 同一类Consumer的集合,这类Consumer通常消费同一类消息且消费逻辑一致。消费者组使得在消息消费方面,实现负载均衡和容错的目标变得非常容易。要注意的是,消费者组的消费者实例必须订阅完全相同的Topic。RocketMQ 支持两种消息模式:集群消费(Clustering)和广播消费(Broadcasting)。
*/
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("please_rename_unique_group_name_4");
/*
* Specify name server addresses.
* <p/>
* 这里可以通知指定环境变量或者设置对象参数的形式指定名字空间服务的地址
*
* Alternatively, you may specify name server addresses via exporting environmental variable: NAMESRV_ADDR
* <pre>
* {@code
* consumer.setNamesrvAddr("name-server1-ip:9876;name-server2-ip:9876");
* }
* </pre>
*/
/*
* Specify where to start in case the specified consumer group is a brand new one.
* 指定消费起始点
*/
consumer.setConsumeFromWhere(ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_FIRST_OFFSET);
/*
* Subscribe one more more topics to consume.
* 指定订阅的 topic 跟 tag,注意后面的是个表达式,可以以 tag1 || tag2 || tag3 传入
*/
consumer.subscribe("TopicTest", "*");
/*
* Register callback to execute on arrival of messages fetched from brokers.
* 注册具体获得消息后的处理方法
*/
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs,
ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
/*
* Launch the consumer instance.
* 启动消费者
*/
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
然后就是看看 start 的过程了
/**
* This method gets internal infrastructure readily to serve. Instances must call this method after configuration.
*
* @throws MQClientException if there is any client error.
*/
@Override
public void start() throws MQClientException {
setConsumerGroup(NamespaceUtil.wrapNamespace(this.getNamespace(), this.consumerGroup));
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.start();
if (null != traceDispatcher) {
try {
traceDispatcher.start(this.getNamesrvAddr(), this.getAccessChannel());
} catch (MQClientException e) {
log.warn("trace dispatcher start failed ", e);
}
}
}
具体的逻辑在this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.start(),这个 defaultMQPushConsumerImpl 就是
/**
* Internal implementation. Most of the functions herein are delegated to it.
*/
protected final transient DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl defaultMQPushConsumerImpl;
public synchronized void start() throws MQClientException {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
log.info("the consumer [{}] start beginning. messageModel={}, isUnitMode={}", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel(), this.defaultMQPushConsumer.isUnitMode());
// 这里比较巧妙,相当于想设立了个屏障,防止并发启动,不过这里并不是悲观锁,也不算个严格的乐观锁
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
this.checkConfig();
this.copySubscription();
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel() == MessageModel.CLUSTERING) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
// 这个mQClientFactory,负责管理client(consumer、producer),并提供多中功能接口供各个Service(Rebalance、PullMessage等)调用;大部分逻辑均在这个类中完成
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getOrCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQPushConsumer, this.rpcHook);
// 这个 rebalanceImpl 主要负责决定,当前的consumer应该从哪些Queue中消费消息;
this.rebalanceImpl.setConsumerGroup(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.rebalanceImpl.setMessageModel(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel());
this.rebalanceImpl.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getAllocateMessageQueueStrategy());
this.rebalanceImpl.setmQClientFactory(this.mQClientFactory);
// 长连接,负责从broker处拉取消息,然后利用ConsumeMessageService回调用户的Listener执行消息消费逻辑
this.pullAPIWrapper = new PullAPIWrapper(
mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), isUnitMode());
this.pullAPIWrapper.registerFilterMessageHook(filterMessageHookList);
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore() != null) {
this.offsetStore = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore();
} else {
switch (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING:
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING:
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.setOffsetStore(this.offsetStore);
}
// offsetStore 维护当前consumer的消费记录(offset);有两种实现,Local和Rmote,Local存储在本地磁盘上,适用于BROADCASTING广播消费模式;而Remote则将消费进度存储在Broker上,适用于CLUSTERING集群消费模式;
this.offsetStore.load();
if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerOrderly) {
this.consumeOrderly = true;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageOrderlyService(this, (MessageListenerOrderly) this.getMessageListenerInner());
} else if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerConcurrently) {
this.consumeOrderly = false;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService(this, (MessageListenerConcurrently) this.getMessageListenerInner());
}
// 实现所谓的"Push-被动"消费机制;从Broker拉取的消息后,封装成ConsumeRequest提交给ConsumeMessageSerivce,此service负责回调用户的Listener消费消息;
this.consumeMessageService.start();
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerConsumer(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), this);
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
this.consumeMessageService.shutdown();
throw new MQClientException("The consumer group[" + this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup()
+ "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.GROUP_NAME_DUPLICATE_URL),
null);
}
mQClientFactory.start();
log.info("the consumer [{}] start OK.", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
throw new MQClientException("The PushConsumer service state not OK, maybe started once, "
+ this.serviceState
+ FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.CLIENT_SERVICE_NOT_OK),
null);
default:
break;
}
this.updateTopicSubscribeInfoWhenSubscriptionChanged();
this.mQClientFactory.checkClientInBroker();
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
this.mQClientFactory.rebalanceImmediately();
}
然后我们往下看主要的目光聚焦mQClientFactory.start()
public void start() throws MQClientException {
synchronized (this) {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
// If not specified,looking address from name server
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
}
// Start request-response channel
// 这里主要是初始化了个网络客户端
this.mQClientAPIImpl.start();
// Start various schedule tasks
// 定时任务
this.startScheduledTask();
// Start pull service
// 这里重点说下
this.pullMessageService.start();
// Start rebalance service
this.rebalanceService.start();
// Start push service
this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultMQProducerImpl().start(false);
log.info("the client factory [{}] start OK", this.clientId);
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", null);
default:
break;
}
}
}
我们来看下这个 pullMessageService,org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.PullMessageService,
![]()
实现了 runnable 接口,
然后可以看到 run 方法
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
接着在看 pullMessage 方法
private void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
final MQConsumerInner consumer = this.mQClientFactory.selectConsumer(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup());
if (consumer != null) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl impl = (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl) consumer;
impl.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} else {
log.warn("No matched consumer for the PullRequest {}, drop it", pullRequest);
}
}
实际上调用了这个方法,这个方法很长,我在代码里注释下下每一段的功能
public void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
final ProcessQueue processQueue = pullRequest.getProcessQueue();
// 这里开始就是检查状态,确定是否往下执行
if (processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.info("the pull request[{}] is dropped.", pullRequest.toString());
return;
}
pullRequest.getProcessQueue().setLastPullTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
this.makeSureStateOK();
} catch (MQClientException e) {
log.warn("pullMessage exception, consumer state not ok", e);
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
return;
}
if (this.isPause()) {
log.warn("consumer was paused, execute pull request later. instanceName={}, group={}", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getInstanceName(), this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_SUSPEND);
return;
}
// 这块其实是个类似于限流的功能块,对消息数量和消息大小做限制
long cachedMessageCount = processQueue.getMsgCount().get();
long cachedMessageSizeInMiB = processQueue.getMsgSize().get() / (1024 * 1024);
if (cachedMessageCount > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the cached message count exceeds the threshold {}, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, count={}, size={} MiB, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), cachedMessageCount, cachedMessageSizeInMiB, pullRequest, queueFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
if (cachedMessageSizeInMiB > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdSizeForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the cached message size exceeds the threshold {} MiB, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, count={}, size={} MiB, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdSizeForQueue(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), cachedMessageCount, cachedMessageSizeInMiB, pullRequest, queueFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
// 若不是顺序消费(即DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.consumeOrderly等于false),则检查ProcessQueue对象的msgTreeMap:TreeMap<Long,MessageExt>变量的第一个key值与最后一个key值之间的差额,该key值表示查询的队列偏移量queueoffset;若差额大于阈值(由DefaultMQPushConsumer. consumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan指定,默认是2000),则调用PullMessageService.executePullRequestLater方法,在50毫秒之后重新将该PullRequest请求放入PullMessageService.pullRequestQueue队列中;并跳出该方法;这里的意思主要就是消息有堆积了,等会再来拉取
if (!this.consumeOrderly) {
if (processQueue.getMaxSpan() > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the queue's messages, span too long, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, maxSpan={}, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), processQueue.getMaxSpan(),
pullRequest, queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
} else {
if (processQueue.isLocked()) {
if (!pullRequest.isLockedFirst()) {
final long offset = this.rebalanceImpl.computePullFromWhere(pullRequest.getMessageQueue());
boolean brokerBusy = offset < pullRequest.getNextOffset();
log.info("the first time to pull message, so fix offset from broker. pullRequest: {} NewOffset: {} brokerBusy: {}",
pullRequest, offset, brokerBusy);
if (brokerBusy) {
log.info("[NOTIFYME]the first time to pull message, but pull request offset larger than broker consume offset. pullRequest: {} NewOffset: {}",
pullRequest, offset);
}
pullRequest.setLockedFirst(true);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(offset);
}
} else {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
log.info("pull message later because not locked in broker, {}", pullRequest);
return;
}
}
// 以PullRequest.messageQueue对象的topic值为参数从RebalanceImpl.subscriptionInner: ConcurrentHashMap, SubscriptionData>中获取对应的SubscriptionData对象,若该对象为null,考虑到并发的关系,调用executePullRequestLater方法,稍后重试;并跳出该方法;
final SubscriptionData subscriptionData = this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().get(pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic());
if (null == subscriptionData) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
log.warn("find the consumer's subscription failed, {}", pullRequest);
return;
}
final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 异步拉取回调,先不讨论细节
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PullResult pullResult) {
if (pullResult != null) {
pullResult = DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), pullResult,
subscriptionData);
switch (pullResult.getPullStatus()) {
case FOUND:
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
long pullRT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestamp;
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullRT(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullRT);
long firstMsgOffset = Long.MAX_VALUE;
if (pullResult.getMsgFoundList() == null || pullResult.getMsgFoundList().isEmpty()) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
} else {
firstMsgOffset = pullResult.getMsgFoundList().get(0).getQueueOffset();
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullTPS(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullResult.getMsgFoundList().size());
boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);
if (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval() > 0) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest,
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval());
} else {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
}
if (pullResult.getNextBeginOffset() < prevRequestOffset
|| firstMsgOffset < prevRequestOffset) {
log.warn(
"[BUG] pull message result maybe data wrong, nextBeginOffset: {} firstMsgOffset: {} prevRequestOffset: {}",
pullResult.getNextBeginOffset(),
firstMsgOffset,
prevRequestOffset);
}
break;
case NO_NEW_MSG:
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.correctTagsOffset(pullRequest);
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
break;
case NO_MATCHED_MSG:
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.correctTagsOffset(pullRequest);
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
break;
case OFFSET_ILLEGAL:
log.warn("the pull request offset illegal, {} {}",
pullRequest.toString(), pullResult.toString());
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
pullRequest.getProcessQueue().setDropped(true);
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executeTaskLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.offsetStore.updateOffset(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
pullRequest.getNextOffset(), false);
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.offsetStore.persist(pullRequest.getMessageQueue());
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.rebalanceImpl.removeProcessQueue(pullRequest.getMessageQueue());
log.warn("fix the pull request offset, {}", pullRequest);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("executeTaskLater Exception", e);
}
}
}, 10000);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void onException(Throwable e) {
if (!pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic().startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("execute the pull request exception", e);
}
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
}
};
// 如果为集群模式,即可置commitOffsetEnable为 true
boolean commitOffsetEnable = false;
long commitOffsetValue = 0L;
if (MessageModel.CLUSTERING == this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
commitOffsetValue = this.offsetStore.readOffset(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_MEMORY);
if (commitOffsetValue > 0) {
commitOffsetEnable = true;
}
}
// 将上面获得的commitOffsetEnable更新到订阅关系里
String subExpression = null;
boolean classFilter = false;
SubscriptionData sd = this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().get(pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic());
if (sd != null) {
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.isPostSubscriptionWhenPull() && !sd.isClassFilterMode()) {
subExpression = sd.getSubString();
}
classFilter = sd.isClassFilterMode();
}
// 组成 sysFlag
int sysFlag = PullSysFlag.buildSysFlag(
commitOffsetEnable, // commitOffset
true, // suspend
subExpression != null, // subscription
classFilter // class filter
);
// 调用真正的拉取消息接口
try {
this.pullAPIWrapper.pullKernelImpl(
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
subExpression,
subscriptionData.getExpressionType(),
subscriptionData.getSubVersion(),
pullRequest.getNextOffset(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize(),
sysFlag,
commitOffsetValue,
BROKER_SUSPEND_MAX_TIME_MILLIS,
CONSUMER_TIMEOUT_MILLIS_WHEN_SUSPEND,
CommunicationMode.ASYNC,
pullCallback
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("pullKernelImpl exception", e);
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
}
}
以下就是拉取消息的底层 api,不够不是特别复杂,主要是在找 broker,和设置请求参数
public PullResult pullKernelImpl(
final MessageQueue mq,
final String subExpression,
final String expressionType,
final long subVersion,
final long offset,
final int maxNums,
final int sysFlag,
final long commitOffset,
final long brokerSuspendMaxTimeMillis,
final long timeoutMillis,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final PullCallback pullCallback
) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult =
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
if (null == findBrokerResult) {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(mq.getTopic());
findBrokerResult =
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
}
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
{
// check version
if (!ExpressionType.isTagType(expressionType)
&& findBrokerResult.getBrokerVersion() < MQVersion.Version.V4_1_0_SNAPSHOT.ordinal()) {
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + ", "
+ findBrokerResult.getBrokerVersion() + "] does not upgrade to support for filter message by " + expressionType, null);
}
}
int sysFlagInner = sysFlag;
if (findBrokerResult.isSlave()) {
sysFlagInner = PullSysFlag.clearCommitOffsetFlag(sysFlagInner);
}
PullMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new PullMessageRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setConsumerGroup(this.consumerGroup);
requestHeader.setTopic(mq.getTopic());
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setQueueOffset(offset);
requestHeader.setMaxMsgNums(maxNums);
requestHeader.setSysFlag(sysFlagInner);
requestHeader.setCommitOffset(commitOffset);
requestHeader.setSuspendTimeoutMillis(brokerSuspendMaxTimeMillis);
requestHeader.setSubscription(subExpression);
requestHeader.setSubVersion(subVersion);
requestHeader.setExpressionType(expressionType);
String brokerAddr = findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr();
if (PullSysFlag.hasClassFilterFlag(sysFlagInner)) {
brokerAddr = computPullFromWhichFilterServer(mq.getTopic(), brokerAddr);
}
PullResult pullResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().pullMessage(
brokerAddr,
requestHeader,
timeoutMillis,
communicationMode,
pullCallback);
return pullResult;
}
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + "] not exist", null);
}
再看下一步的
public PullResult pullMessage(
final String addr,
final PullMessageRequestHeader requestHeader,
final long timeoutMillis,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final PullCallback pullCallback
) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.PULL_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
switch (communicationMode) {
case ONEWAY:
assert false;
return null;
case ASYNC:
this.pullMessageAsync(addr, request, timeoutMillis, pullCallback);
return null;
case SYNC:
return this.pullMessageSync(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
default:
assert false;
break;
}
return null;
}
通过 communicationMode 判断是同步拉取还是异步拉取,异步就调用
private void pullMessageAsync(
final String addr,
final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis,
final PullCallback pullCallback
) throws RemotingException, InterruptedException {
this.remotingClient.invokeAsync(addr, request, timeoutMillis, new InvokeCallback() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
异步
RemotingCommand response = responseFuture.getResponseCommand();
if (response != null) {
try {
PullResult pullResult = MQClientAPIImpl.this.processPullResponse(response);
assert pullResult != null;
pullCallback.onSuccess(pullResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
pullCallback.onException(e);
}
} else {
if (!responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
pullCallback.onException(new MQClientException("send request failed to " + addr + ". Request: " + request, responseFuture.getCause()));
} else if (responseFuture.isTimeout()) {
pullCallback.onException(new MQClientException("wait response from " + addr + " timeout :" + responseFuture.getTimeoutMillis() + "ms" + ". Request: " + request,
responseFuture.getCause()));
} else {
pullCallback.onException(new MQClientException("unknown reason. addr: " + addr + ", timeoutMillis: " + timeoutMillis + ". Request: " + request, responseFuture.getCause()));
}
}
}
});
}
并且会调用前面 pullCallback 的onSuccess和onException方法,同步的就是调用
private PullResult pullMessageSync(
final String addr,
final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis
) throws RemotingException, InterruptedException, MQBrokerException {
RemotingCommand response = this.remotingClient.invokeSync(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
assert response != null;
return this.processPullResponse(response);
}
然后就是这个 remotingClient 的 invokeAsync 跟 invokeSync 方法
@Override
public void invokeAsync(String addr, RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis, InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
RemotingSendRequestException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
try {
doBeforeRpcHooks(addr, request);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsync call timeout");
}
this.invokeAsyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback);
} catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
log.warn("invokeAsync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw e;
}
} else {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
}
}
@Override
public RemotingCommand invokeSync(String addr, final RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
try {
doBeforeRpcHooks(addr, request);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeSync call timeout");
}
RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), request, response);
return response;
} catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
log.warn("invokeSync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw e;
} catch (RemotingTimeoutException e) {
if (nettyClientConfig.isClientCloseSocketIfTimeout()) {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
log.warn("invokeSync: close socket because of timeout, {}ms, {}", timeoutMillis, addr);
}
log.warn("invokeSync: wait response timeout exception, the channel[{}]", addr);
throw e;
}
} else {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
}
}
再往下看
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
同步跟异步都是会把结果用ResponseFuture抱起来
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
// 区别是同步的是在这等待
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
public void invokeAsyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreAsync.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreAsync);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
once.release();
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeAsyncImpl call timeout");
}
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <{}> failed.", RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel));
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
responseFuture.release();
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel) + "> Exception", e);
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info =
String.format("invokeAsyncImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreAsync.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreAsync.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
]]>














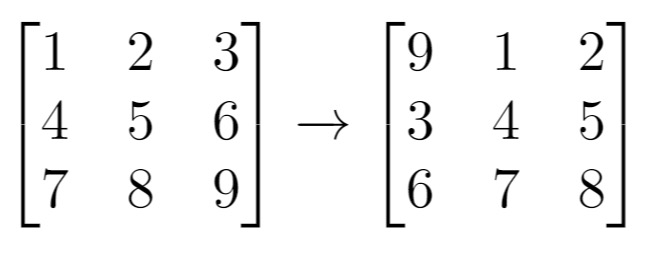







![9G5FE[9%@7%G(B`Q7]E)5@R.png](https://ooo.0o0.ooo/2016/08/10/57aac43029559.png)










 再看这个图,我们发现在这的时候还没有进行替换
再看这个图,我们发现在这的时候还没有进行替换 好像是这里了
好像是这里了




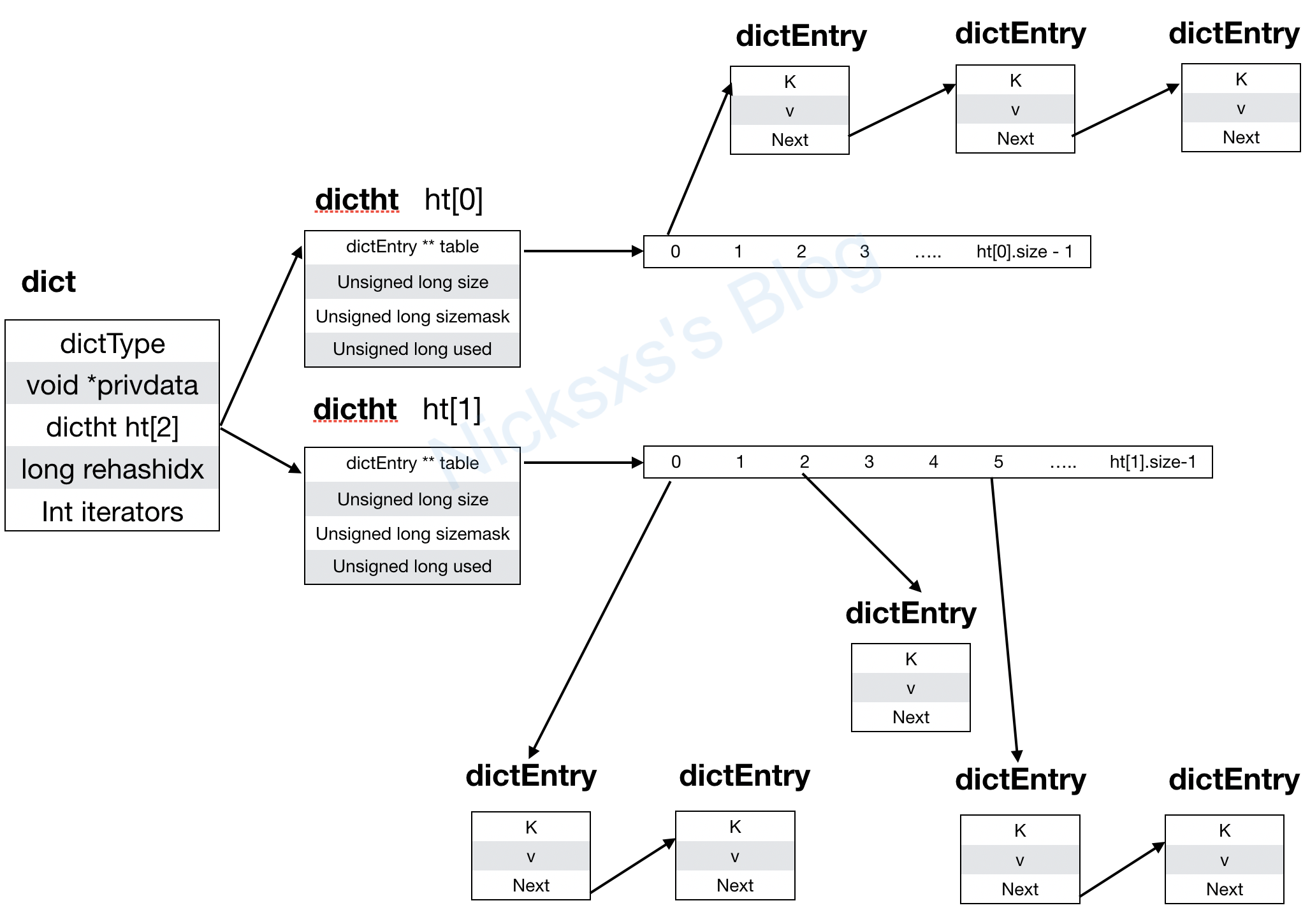




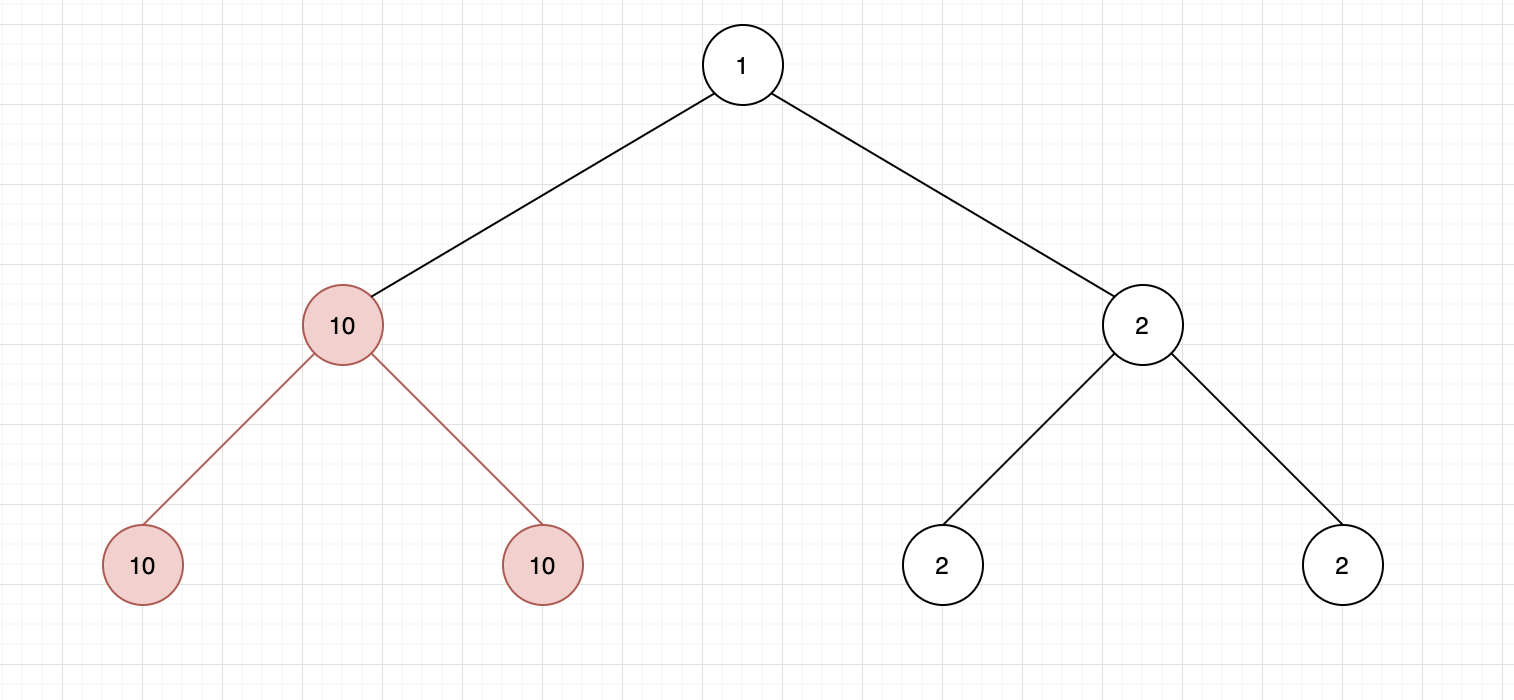
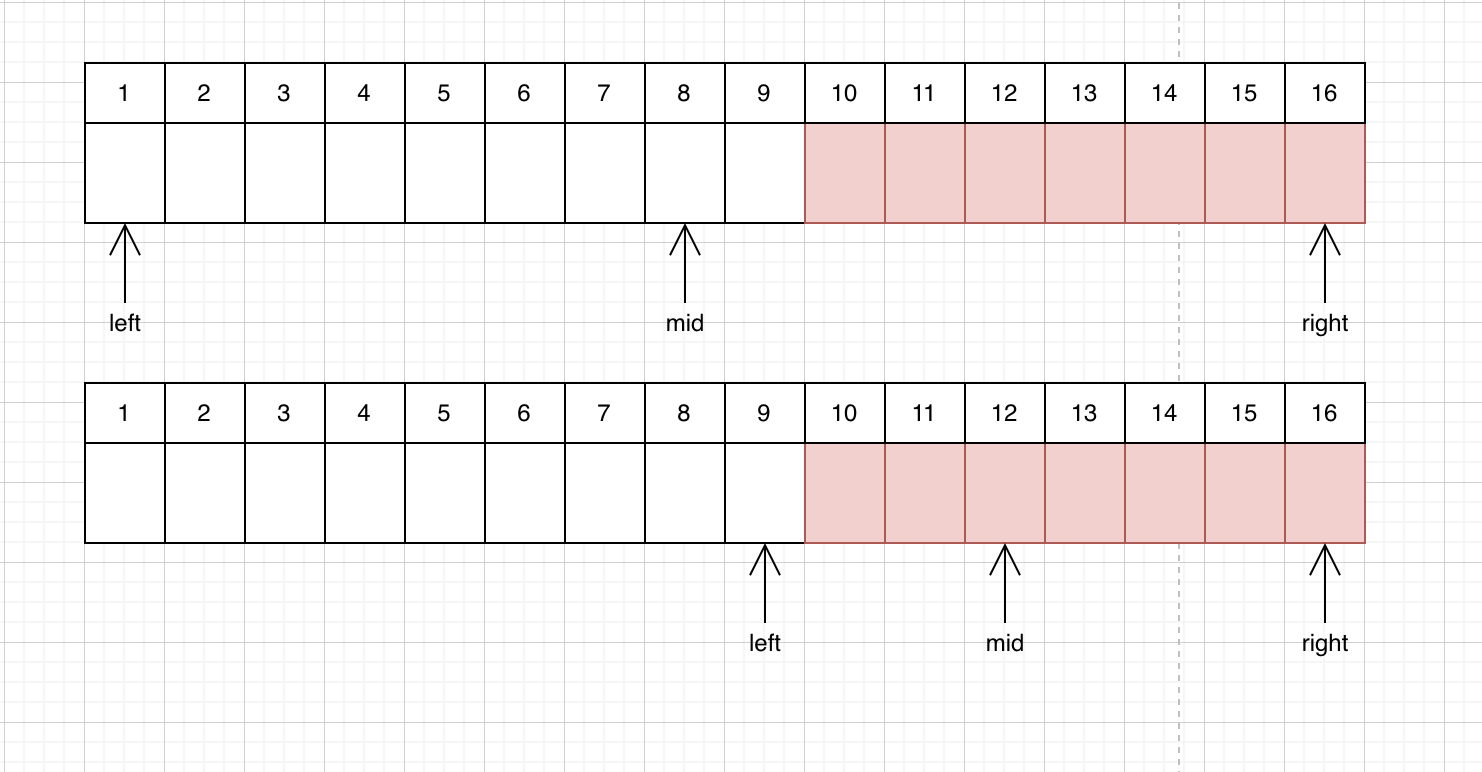
 ,图中一共有四个槽的存储空间,依次访问顺序是 A B C D E D F,
,图中一共有四个槽的存储空间,依次访问顺序是 A B C D E D F,













user2:
user3: