Tomcat 会把请求委托到org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doService
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
然后就是调用org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
看下这里的逻辑
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
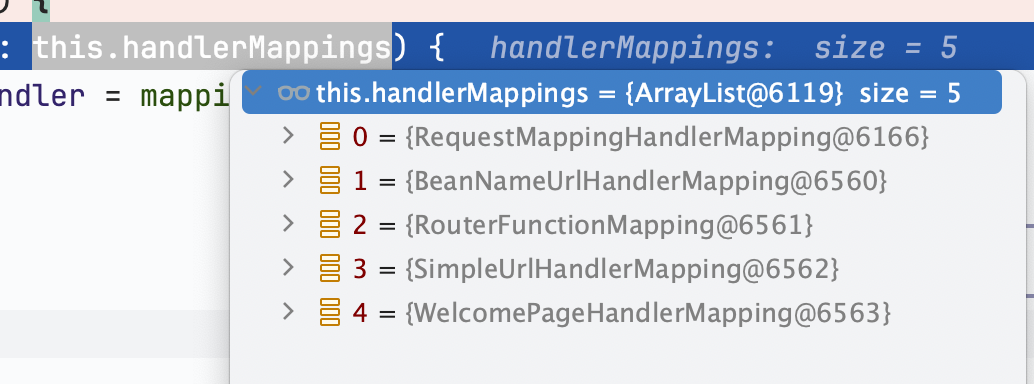
可以看到有这些 HandlerMapping
![]()
而这里面就是前面提到过的org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
从这就能找到具体的 Handler
com.nicksxs.spbdemo.controller.DemoController#test()
这就是我简单的示例代码
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public DemoResponse test() {
String item = "{\"id\": 1, \"name\": \"nick\"}";
ParserConfig parserConfig = ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance();
parserConfig.propertyNamingStrategy = PropertyNamingStrategy.SnakeCase;
DemoResponse response = JSON.parseObject(item, DemoResponse.class, parserConfig);
return response;
}
再获取适配器,org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
正好这个适配器是调用的父类的 supports 方法
@Override
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));
}
而我这个com.nicksxs.spbdemo.controller.DemoController#test()就是个包装好的 HandlerMethod
然后就是调用 ha 的 handle 方法,也是通过模板方法,实际调用的是
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handle
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
然后调用 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#handleInternal
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
继续调用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#invokeHandlerMethod
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
稍微在看一眼
第一步是org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#createInvocableHandlerMethod
protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod createInvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
}
第二步是org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod#ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod)
public ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
super(handlerMethod);
}
第三部是org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod#InvocableHandlerMethod(org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod)
public InvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
super(handlerMethod);
}
第四步是org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod#HandlerMethod(org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod)
protected HandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod is required");
this.bean = handlerMethod.bean;
this.beanFactory = handlerMethod.beanFactory;
this.beanType = handlerMethod.beanType;
this.method = handlerMethod.method;
this.bridgedMethod = handlerMethod.bridgedMethod;
this.parameters = handlerMethod.parameters;
this.responseStatus = handlerMethod.responseStatus;
this.responseStatusReason = handlerMethod.responseStatusReason;
this.description = handlerMethod.description;
this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod = handlerMethod.resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
}
这是个继承关系,一直调用到最顶层的父类的构造方法,其实就是拷贝,然后继续调用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod#invokeAndHandle
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
}
继续调用 org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod#invokeForRequest
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
return doInvoke(args);
}
来到了最核心处 org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod#doInvoke
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
Method method = getBridgedMethod();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
try {
if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);
}
return method.invoke(getBean(), args);
}